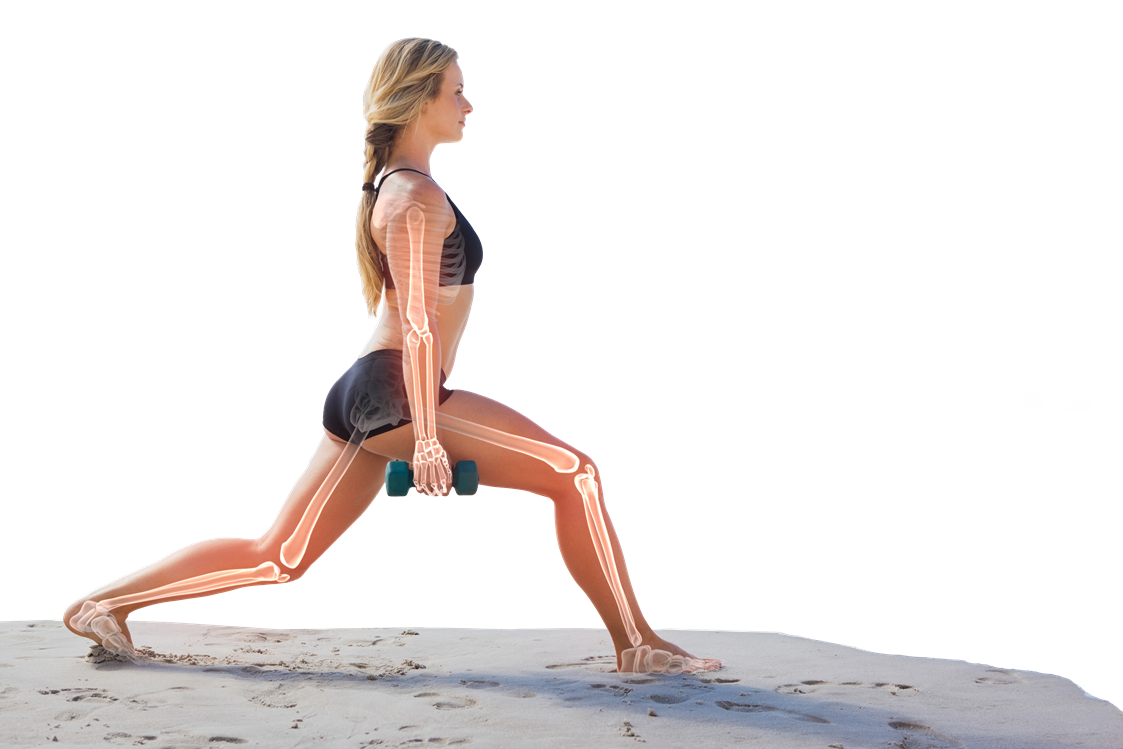
What should we know about joints and bones ?
Joints
The skeleton is a movement system consisting of 206 bones, cartilages and ligaments. All of this serves as a support for skeletal muscles and for the protection of internal organs. The skeletal system consists of individual bones consisting of calcium, phosphorus and fibrous substance – collagen. The joint connects two or more bones, while allowing movement.
Simple joints combine only two bones, as in the shoulder, more than two bones joining compound joints, such as in the knee or wrist. Depending on the mobility, we distinguish more types of joints, for example, to illustrate the example of the hip, which represents a ball joint allowing a wide range of movements, or finger joints made up of simple cylindrical joints designed for bending and stretching only.
All kinds of joints allow the smooth cartilage to move, which covers the skeletal tip and the synovial membrane that lifts the joint and makes it slippery.
Cartilage
Cartilage is an important structural component of the body. It is a connective tissue that serves to strengthen surrounding tissues. It is part of the musculoskeletal system and covers the joint surfaces of most joints. It is vascular, very stiff, but also quite flexible and able to cope with vibrations. Thanks to its elastic structure it significantly reduces the friction of the contact joints. If the cartilage becomes worn or damaged, its function is impaired. Over time, the bone is damaged under the cartilage, which is accompanied by considerable pain. Joint cartilage is subject to degenerative changes, its damage is irreversible and can not be corrected.
To avoid arthritis, it is necessary to have healthy cartilage. The cartilage consists, inter alia, of chondrocytes, collagen and elastic fibers, and intercellular matter. One of the basic building blocks of cartilage and intercellular material, which we can simply add to the diet, are collagen, chondroitin and glucosamine. Collagen alone produces vitamin C and MSM (organic form of sulfur).
Joints illness
Locomotive disease can significantly affect the quality of life of a person. Restrictions in movement are often accompanied by pain, stiffness or various physical disabilities. The movement system is formed by muscles, bones, joints, ligaments and tendons. The individual components of this system are in a dynamic balance and change their shape and structure depending on the external influences, stress and load of the organism. The locomotive disorders are divided from the anatomical point of view into diseases affecting the muscles, bones or joints. In the case of joints, the most common disease is osteoarthritis.
It is a degenerative joint disease where the disease changes primarily affect the cartilage. In addition to subjective difficulties, mobility is reduced to permanent disability. Osteoarthritis begins first without any difficulty in the 2nd or 3rd decade of life and eventually affects practically all persons over 70 years of age.
Risk factors include obesity, lifestyle, and genetics also play a role. Osteoarthritis most commonly afflicts large joints, knees and hip joints. Arthrosis affects shoulder joints and joints on hands and feet.
What causes movement difficulties ?
Arthrosis
Arthrosis is characterized by degenerative joint changes, the cause of which is the excessive loading of the joints. There is progressive destruction of the articular cartilage and the formation of small growths. The manifestation of arthrosis is joint pain, stiffness and reduced mobility.
Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of joints, can be of infectious or non-infectious origin. It is not related to the load on the joints or their wear. Arthritis is accompanied by pain, swelling and increased joint temperature. Rheumatoid atritis is manifested by morning stiffness of small joints.
Stretched ligaments
The knee links ensure the stability of the joints and enable their loading. Knee ligament injury can occur during physical activity. The manifestation is a painful knee that is swollen and whose momentum is limited. The cause is micro cracks that arise when stretching the ligaments.
Tendons inflammation
The cause of tendonitis is excessive muscle loading without adequate regeneration. It is often manifested in athletes, people with physically demanding jobs, or when overloaded with a one-off motion. The risk factor may be not to lift the muscles before exercise and their insufficient warming up.
Anatomy of knee joint
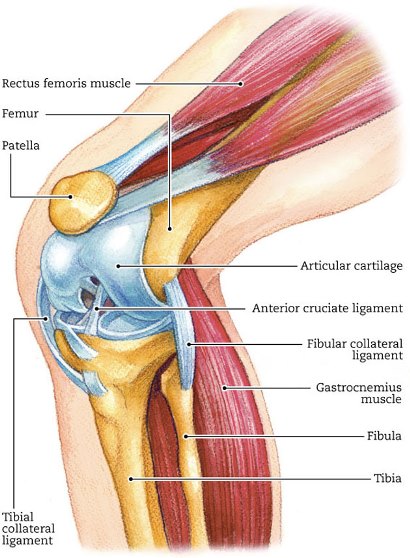
The knee is the most complex joint in the human body. It connects the femur, the tibia and the knee (the patella).
On the front of the femur there is a four-headed muscle that extends the knee. The muscles on the back of the femur (hamstring) allow the knee to cringe. Patella has the function of a quadriceps lever and increases its effectiveness. When the knee moves, the surface of the tympanum and femur slides and the heel moves up and down.
The space between the bones is filled with articular cartilage that balances the vibrations and reduces the friction in the joint surfaces. Inside the knee is a lining – a synovia that produces fluid to help reduce friction of the joints while helping to nourish the cartilage. There are two types of cartilage in the knee – joint cartilage and meniscus. The articular cartilage covers the surface of the joints. Meniscus helps to distribute the load, improves the stability of the knee and protects the articular cartilage. The connective tissue is attached to the tibia and the femur, connects the bones to each other and ensures the stability of the joints at different stages of movement.
The knee is one of the most important joint in the human body, it is exposed to considerable strain and its damage can also mean permanent complications.
Healthy lifestyle

What can you do for your healthy locomotive system? How to help your lifestyle with your aching joints or backs? What to add? What to lose? Inspire and indulge in a change.
Healthy lifestyle, a healthy diet without unnecessary fats and sugars, a lot of movement while eliminating inappropriate physical activity or unilateral loads – this can be a way to protect your joints and bones and enjoy a comfortable and painless movement.
Prevention

The causes of arthritis are not fully elucidated and its treatment never leads to complete healing. Precautions should therefore be taken. The basis of prevention of joint diseases is exercise.
Maintaining physical fitness, optimal weight and a healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals and collagen. A complex formula with a combination of everything needed for joint nutrition is provided by the Arthrosin supplement. Do you put it into your new lifestyle?
Diet for healthy joints
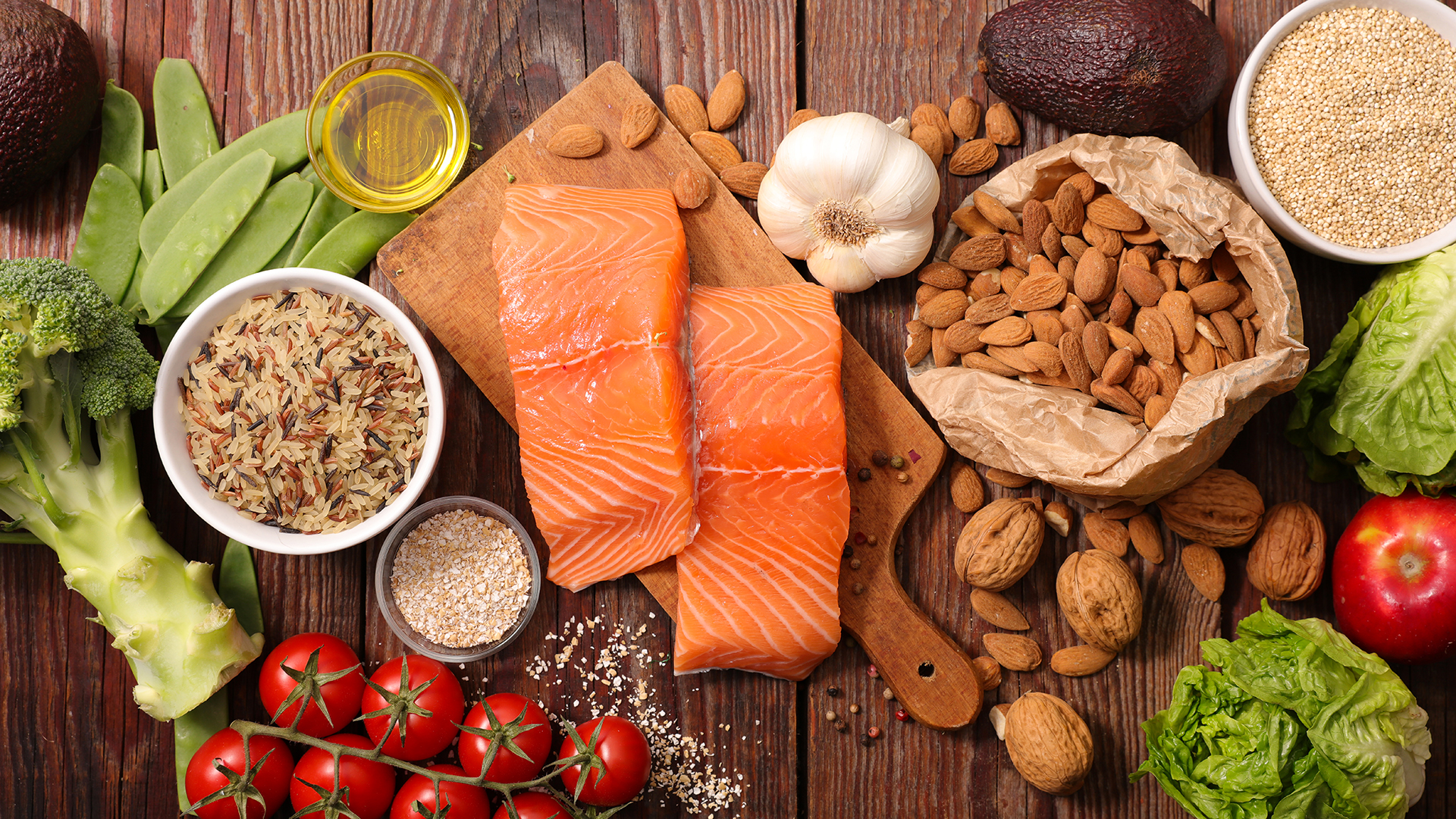

Treat healthy food and healthy joints. Add to your diet what knuckles need and give up what damages them. Inspire and give your joints a new chance.
Joint illnesses are often caused by inflammation, so it is advisable to enrich your diet with antioxidants such as vitamin C, which inhibits the secretion of histamine from the vascular walls into the joints, which then plays a role in inflammation. The basis for healthy cartilage is collagen, do not forget about it, eat with common sense, and when, perhaps, just rubber teddy bears that are full of collagen. Eat plenty of food rich in essential fatty acids, which also help to prevent inflammation and relieve arthritis.
An excellent source of vitamin C is fresh fruit and vegetables, perhaps surprisingly potatoes, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts or broccoli. A natural source of collagen is, for example, beef shin or mutton. Increased meat intake in articular diseases is not appropriate due to the occurrence of arachidonic acid, which is considered to be co-responsible for joint inflammation. Collagen should therefore be supplemented otherwise. Fatty fish and various seeds, olives, soy, corn or beans are rich in essential fatty acids, you could certainly put them in your diet.
On the contrary, sweets are very inappropriate, because high blood glucose levels aggravate inflammation. Because of the arachidonic acid mentioned above, beef, eggs or dairy products are not recommended too much. Frozen and burnt foods should also be restricted. Due to high salt content, you can deny a variety of semi-finished products, salted snacks and chips.
In the case of joint problems, it is recommended to try an “anti-inflammatory diet”, which comes from Mediterranean which contains lots of fish, olive oil and vegetables.
Provide comfort to your joints
Artrosin contains ingredients effective for the health of joints, bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments. The high dose of pure glucosamine in combination with chondoitin, MSM, Boswelii Seratta, enhanced by the effective Flexi complex (type II collagen, vitamin C, turmeric and manganese), has a positive effect on the state of the locomotor system.
The ingredients in Arthrosin help to regenerate the bones and increase their resistance. They nourish joints and care for their health and functionality. They help relieve pain and inflammation because they work against their cause and do not just solve their symptoms.
Arthrosin is the right choice for your joints!